Year-on-year
Year-on-year is a method of comparing financial or other measurable data from one period to the same period in the previous year. This comparison allows you to evaluate growth or decline on an annual basis. Providing insights into trends and performance changes over time. It is a mildly used metric in finance, economics, and other fields to assess how a company’s performance is improving or becoming worse.
Why Is Year-on-year Growth Important
It Accounts for Seasonal Fluctuations
Some companies’ performances fluctuate from month to month, so analysing performance at the same time of the year creates a useful comparison.
Fluctuations indicate busy seasons; for instance, if your business is a holiday resort, business will be booming during school holidays. If you sell swimwear, this might only be popular during the summer months. Entrepreneurs who specialise in renovation services might find their busiest time of the year is during dry months.
It Allows Company Leaders to Establish Baselines
By using year-on-year comparisons for several years in a row, a company’s leadership team can identify growth trends and estimate a baseline revenue or other metric for forecasting.
Looking beyond the seasonal fluctuations, leadership can see if there is true growth in the business as it compares the same time frame for the current year with previous years.
It is Useful for Investors
The goal of investing in a company is to support the company’s year-on-year growth and earn dividends, so investors can use the year-on-year comparison to predict the value of their returns and decide whether the company is a good fit for their investment goals.
How Year-on-year Works
Year-on-year compares a company's financial performance in one period with its numbers for the same period one year earlier. This is considered more informative than a month-to-month comparison, which often reflects seasonal trends. Common year-on-year comparisons include annual and quarterly as well as monthly performance.
How it Works
Select a Metric
Choose the specific data point you want to analyse, for example, revenue, profit, expense, or sales volume.
Choose a Period
Select the specific period you want to compare, for example, a quarter, a month, or a full year.
Gather the Data
Obtain the data for both the current period and the corresponding period in the previous year.
Calculate the Change
Subtract the previous year’s value from the current year’s value and divide the result by the previous year’s value. Multiply by 100 to express the change as a percentage.
Year-on-year Formula
The formula used to calculate the year-on-year growth divides the current period value by the prior period value and then subtracts one.
Year-on-year growth = (Current period value ÷ prior period value) - 1
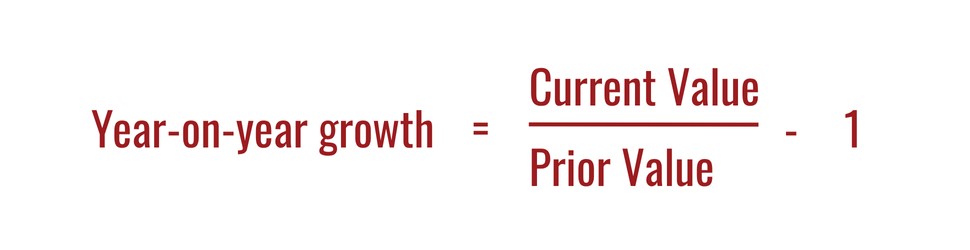
(1 is subtracted from the divided value to factor in the previous year’s growth rate. One implies that you don’t start from 0; you start from 1.)
Benefits of Year-on-Year
Year-on-year measurements facilitate the cross-comparison of sets of data. For a company’s first-quarter revenue using year-on-year data, a financial analyst or an investor can compare years of first-quarter revenue data and quickly ascertain whether a company’s revenue is increasing or decreasing.
Uses of Year-on-year
Year-on-year comparisons are popular when analysing a company’s performance because they help mitigate seasonality, a factor that can influence most businesses. Sales, profits, and other financial metrics change during different periods of the year because most lines of business have a peak season and a low-demand season.
For example, retailers have a peak demand season during the holiday shopping season, which falls in the fourth quarter of the year. To accurately quantify a company’s performance, it makes sense to compare revenue and profits year-on-year.
Year-on-year is a useful tool for financial analysts, corporations, and investors. It allows the comparison of financial figures from one point in time to the same point a year prior. It paints a clear picture of performance.

